If you’re reading this because you want to learn more about stocks and how to invest, check out The Motley Fool’s Broker Center and get started today. A leveraged buyout (LBO) is a transaction in which a company or business is acquired using a significant amount of borrowed money (leverage) to meet the cost of acquisition.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
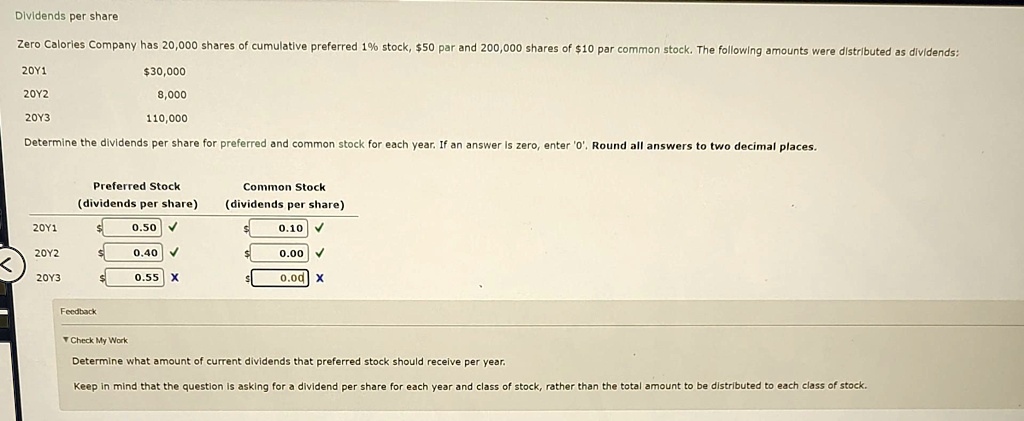
This approach not only builds trust among investors but also highlights the importance of dividends, in reducing risk, for shareholders. In addition, preferred shareholders receive a fixed payment that’s similar to a bond issued by the company. The payment is in the form of a quarterly, monthly, or yearly dividend, depending on the company’s policy, and is the basis of the valuation method for a preferred share. Preferred shares have the qualities of stocks and bonds, which makes their valuation a little different than common shares. The owners of preferred shares are part owners of the company in proportion to the held stocks, just like common shareholders. Preferreds have fixed dividends and, although they are never guaranteed, the issuer has a greater obligation to pay them.
Conversion or Issuance During the Period
This is because the fixed payment is based on a real rate of interest and is typically unadjusted for inflation. In year three, the economy booms, allowing the company to resume dividends. The cumulative preferred stock shareholders must be paid the $900 in arrears in addition to the current dividend of $600. Once all cumulative shareholders receive the $1,500 due per share, the company may consider paying dividends to other classes of shareholders. Essentially, they pay cumulative dividends that build up a ledger of owed payments over time.
Cumulative Dividend Yield
- The preferred shares also carry a clause on extra dividends for participating preferred stock, which is triggered whenever the dividend for common shares exceeds that of the preferred shares.
- On the other hand, non-cumulative dividends do not accumulate; if not paid in a given period, they are forfeited.
- Participating preferred stock is rarely issued, but one way in which it is used is as a poison pill.
- The higher the ratio, the less trouble the company will have in making its required dividend payments.
With preferreds, the investor is standing closer to the front of the line for payment than common shareholders, although not by much. Preferred dividends are link to preferred shares, which are accounting cycle steps and examples what is accounting cycle video and lesson transcript a type of equity in the company, although these shareholders do not have any voting rights. Most shares do not have a maturity date, and if they do, then they are quite far in the future.
Cumulative Dividends vs Non-Cumulative
We Fools may not all hold the same opinions, but we all believe that considering a diverse range of insights makes us better investors. Founded in 1993, The Motley Fool is a financial services company dedicated to making the world smarter, happier, and richer. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly.
That’s why we call it perpetuity because the dividend payment is equal and paid for an infinite period. Cumulative dividends are intended to ensure investors receive at least a minimum return on their investment in the company. Cumulative dividend provisions may contain limitations, such as being payable only if the company liquidates. A company that issues cumulative preferred stock must disclose any accumulated, unpaid dividends in its financial statements.
Preferred dividends are the dividends that are accrued paid on a company’s preferred stock. If the company is unable to pay all the dividends, then claims to any preferred dividends will take precedence over claims to dividends on common shares. This can occur when a company decides to suspend dividend payments during tough financial times, as we saw with several companies during the 2008 financial crisis. If a similar situation occurs with any preferred stocks you own, here’s how to calculate the cumulative dividends owed to you. Ex-dividend refers to the date after which a buyer of a stock will not receive the upcoming dividend payment. Cumulative dividend refers to a type of preferred stock where any unpaid dividends accrue and must be paid before common shareholders receive dividends.
Callable preferred stock results in higher preferred dividends, as investors are sacrificing long-term security. If the preferred stock is retired at the call price, future preferred dividends may be included in the repurchase. Convertible preferred stock has lower preferred dividends, as the investor receives the additional of converting the preferred stock to common stock. The dividends for preferred stocks are, by definition, determined in advance and paid out before any dividend for the company’s common stock is determined. The dividend may be a set percentage or may be tied to a particular benchmark interest rate.
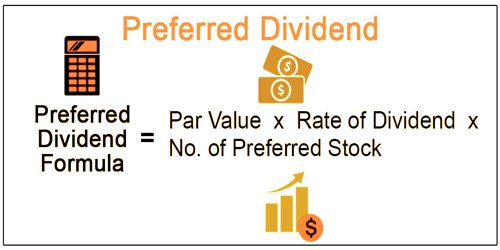
Finally, to determine the amount of money you’ll receive, take the appropriate dividend (annual or quarterly) and multiply it by the number of shares you own. Investors can use this equation to figure out the dividends due on a stock by considering any dividends already paid and including the outstanding dividends accumulated over a specific period. Generally, the dividend is fixed as a percentage of the share price or a dollar amount. On the other hand, if conversion is assumed, the dividends would not have been paid and, accordingly, are not deducted from net income. Through an online broker or by contacting your personal broker at a full-service brokerage. In this article, we look at preferred shares and compare them to some better-known investment vehicles.
However, because they are shares and not loans to the company, there is an equity component as well. If you want to determine how much your dividend will be on a quarterly basis (assuming your preferred stock pays quarterly), simply divide this result by four. Your preferred stock’s dividend rate and par value can be found in the issuing company’s preferred stock prospectus, so the first step is to locate this information. The number of common shares issued at conversion is included in the weighted average of outstanding shares. For the period prior to conversion, the common shares that would have been outstanding are weighted by the appropriate fraction of the year.

